Introduction
In today's fiercely competitive global market, achieving quality excellence is a crucial aspect for any organization aiming to stay ahead of the curve. The International Automotive Task Force (IATF) has set standards and requirements to ensure high-quality products and services in the automotive industry. Among all the existing standards, IATF 16949:2016 stands out as a powerful quality management system that emphasizes the process approach, risk based thinking and enabling organizations to streamline their operations and optimize efficiency.
Understanding the Process Approach
The process approach is a fundamental concept in IATF 16949:2016 that focuses on understanding, managing, and optimizing various interconnected processes within an organization. Unlike traditional management systems that treat processes in isolation, the process approach views them as a coherent system where outputs from one process become inputs for others. This holistic perspective enhances the organization's ability to identify and address issues systematically, leading to improved overall performance and quality excellence.
Key Principles of the Process Approach

1. Customer Focus
The process approach starts with understanding the needs and expectations of customers. By identifying these requirements, organizations can align their processes to deliver products and services that consistently meet or exceed customer expectations. Customer satisfaction is at the heart of the process approach, driving organizations to continuously improve their processes to enhance customer experience.
2. Leadership and Commitment
Top management's commitment is critical to the successful implementation of the process approach. Leaders must provide the necessary resources, support, and direction to ensure that the organization embraces a culture of quality excellence. Their involvement sets the tone for the entire organization and emphasizes the importance of process optimization.
3. Employee Involvement and Empowerment
Employees are the backbone of any organization, and their active involvement and empowerment are essential for the process approach to thrive. Engaged employees contribute valuable insights, identify opportunities for improvement, and play a significant role in the successful execution of processes.
4. Process Approach
Organizations should understand their processes as a series of interrelated activities that contribute to the achievement of objectives. A process approach helps in managing and improving these activities systematically.
5. Continuous Improvement
The process approach is built on the foundation of continuous improvement. Organizations must continuously review and refine their processes to achieve better efficiency, productivity, and quality outcomes. The pursuit of excellence is never-ending, and embracing a culture of continuous improvement is vital for sustained success.
6. Evidence-Based Decision Making:
Decisions should be based on the analysis and evaluation of data and information. Using evidence to make informed decisions contributes to the overall effectiveness of the QMS
7. Relationship Management:
Organizations depend on relationships with interested parties such as customers, suppliers, and regulators. Managing these relationships effectively can lead to improved performance, innovation, and mutual benefits.
Implementing the Process Approach
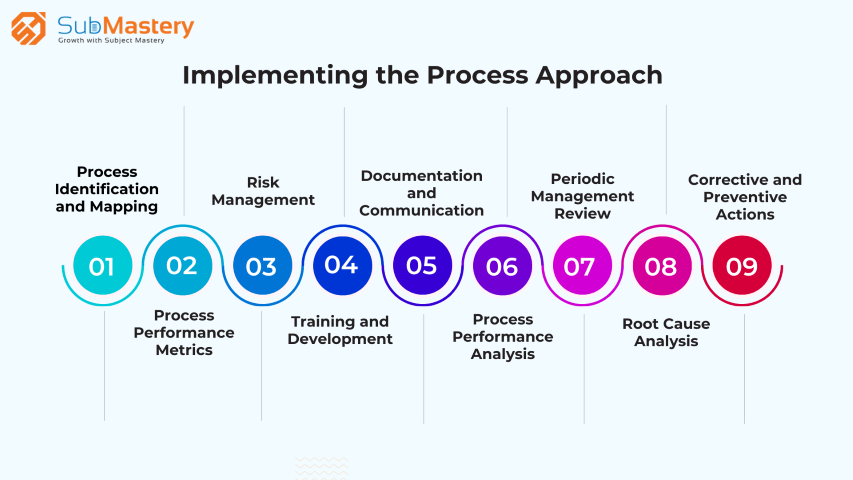
1. Process Identification and Mapping
The first step in implementing the process approach is to identify and map out the key processes within the organization. This involves a comprehensive assessment of the activities, inputs, outputs, and stakeholders associated with each process. Process mapping provides a visual representation of the interconnectedness between different processes, helping organizations understand how they contribute to the overall value chain.
2. Process Performance Metrics
Once the processes are identified, it's crucial to establish relevant performance metrics for each one. These metrics should align with the organization's strategic goals and focus on aspects such as efficiency, effectiveness, and customer satisfaction. Regularly monitoring and analyzing these metrics enables organizations to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
3. Risk Management
The process approach emphasizes proactive risk management. Organizations must identify potential risks associated with their processes and develop strategies to mitigate them. Implementing preventive measures ensures that potential issues are addressed before they escalate, safeguarding the organization's performance and reputation.
4. Training and Development
For the process approach to succeed, employees need to be equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge. Training programs should focus on building competency and awareness of the process approach principles. Properly trained employees are more likely to embrace the process approach and actively contribute to its implementation.
5. Documentation and Communication
Comprehensive documentation of processes, procedures, and work instructions is a crucial aspect of the process approach. Clear communication ensures that all employees understand their roles, responsibilities, and the interdependencies between processes. Transparent communication fosters collaboration and helps in resolving issues efficiently.
6. Process Performance Analysis
Regularly analysing process performance data is essential for identifying trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Organizations should use tools such as statistical process control (SPC) and process capability indices to assess process stability and capability. This data-driven approach enables organizations to make informed decisions and optimize processes continually.
7. Periodic Management Review
Periodic management reviews are essential to assess the effectiveness of the process approach implementation. These reviews provide a platform for top management to evaluate progress, discuss challenges, and make strategic decisions related to process optimization and quality improvement.
8. Root Cause Analysis
In the pursuit of quality excellence, it's crucial to identify and address the root causes of any deviations or non-conformances within processes. Root cause analysis involves systematic investigation and problem-solving to prevent recurring issues. Identifying and resolving root causes leads to more robust processes and improved product/service quality.
9. Corrective and Preventive Actions
When issues arise, taking corrective actions is essential to rectify immediate problems. However, the process approach goes beyond just correcting problems; it also focuses on implementing preventive actions to avoid similar issues in the future. This proactive approach ensures that the organization is always striving for betterment.
Benefits of the Process Approach
The process approach, when implemented effectively, offers numerous benefits to organizations striving for quality excellence:
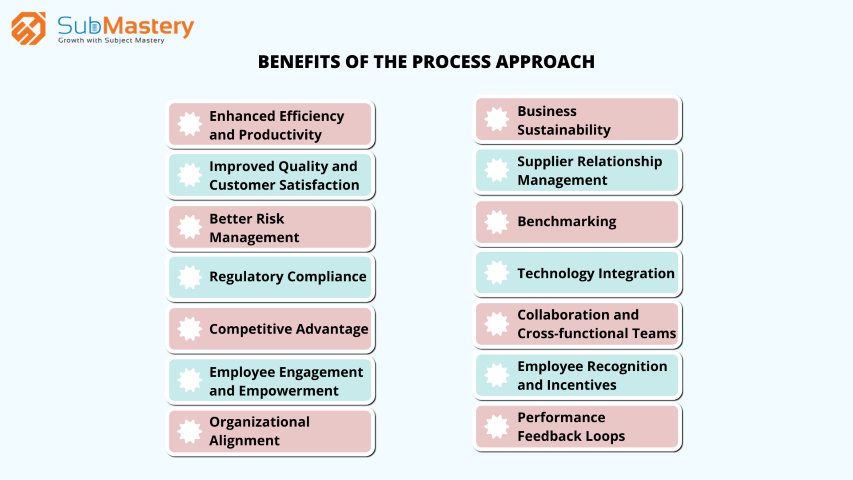
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
By optimizing processes, organizations can eliminate redundancies and inefficiencies, leading to enhanced productivity. Streamlining operations translates into cost savings, reduced lead times, and increased throughput.
2. Improved Quality and Customer Satisfaction
A process-oriented approach ensures consistent quality outputs, meeting customer expectations and enhancing satisfaction. Delivering high-quality products and services fosters long-term customer loyalty and positive brand perception.
3. Better Risk Management
Identifying and managing risks within processes allows organizations to prevent potential issues and minimize disruptions. Proactive risk management leads to a more resilient and reliable operation.
4. Regulatory Compliance
IATF 16949:2016 certification signifies that an organization adheres to the highest automotive quality standards. The process approach aids in complying with these requirements, facilitating smoother audits and assessments.
5. Competitive Advantage
Organizations that successfully implement the process approach gain a competitive edge. Improved efficiency, higher quality, and better customer satisfaction contribute to differentiating them from competitors.
6. Employee Engagement and Empowerment
Involving employees in the process approach fosters a culture of ownership and empowerment. Engaged employees are more committed to delivering excellent results and actively contribute to process improvements.
7. Organizational Alignment
The process approach promotes alignment across various functions and departments within an organization. This alignment ensures that everyone is working towards common objectives, driving the organization forward cohesively.
8. Business Sustainability
By continuously improving processes, organizations build resilience and adaptability. This sustainability ensures that the organization remains viable and relevant in the face of changing market dynamics and customer preferences.
09. Supplier Relationship Management
An integral part of the process approach is maintaining strong relationships with suppliers. Organizations should work collaboratively with their suppliers to ensure that the quality of inputs and materials is consistent. A well-managed supplier network enhances process efficiency and reduces the risk of non-conformities.
10. Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves comparing an organization's processes and performance against industry best practices or competitors. This practice helps identify areas where the organization can improve and sets performance goals for continual improvement. By learning from the best, organizations can refine their processes and achieve superior results.
11. Technology Integration
Leveraging technology can significantly enhance the process approach. Implementing advanced software, automation, and data analytics tools can streamline processes, improve data accuracy, and identify optimization opportunities. Technology integration fosters a data-driven culture, enabling organizations to make more informed decisions.
12. Collaboration and Cross-functional Teams
The process approach encourages collaboration among different departments and teams. Cross-functional teams can bring diverse perspectives and expertise to process improvement initiatives. This interdisciplinary approach fosters innovation and creativity, leading to breakthroughs in efficiency and quality.
13. Employee Recognition and Incentives
Recognizing and rewarding employees for their contributions to process improvement is vital for sustaining the process approach. Incentive programs can motivate employees to actively participate in process optimization, creating a culture of continuous improvement.
14. Performance Feedback Loops
Establishing feedback loops is essential for monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of process improvements. Regularly seeking feedback from employees, customers, and other stakeholders helps identify areas for further enhancement and ensures that the organization remains agile in responding to changing requirements.
Case Study: Implementing the Process Approach in an Automotive Manufacturer
To illustrate the practical impact of the process approach, let's consider a case study of an automotive manufacturer, ABC Motors. The company decided to embrace IATF 16949:2016 and adopt the process approach to enhance its operations and deliver superior products to customers.
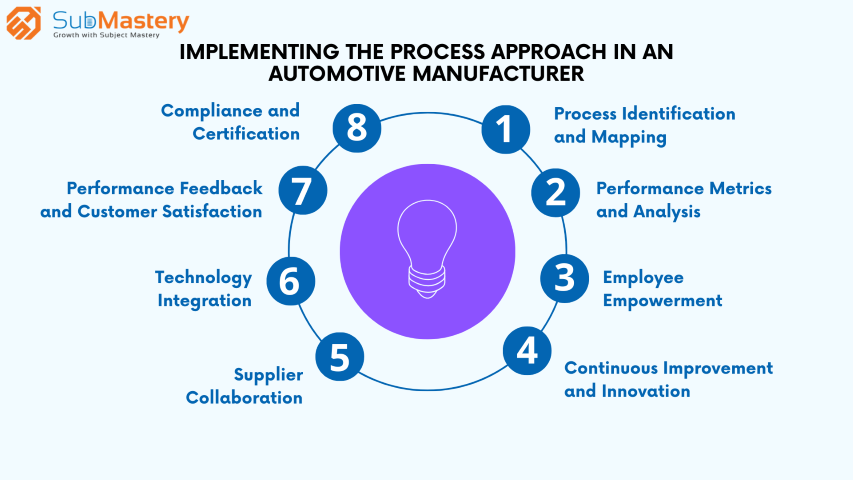
Step 1: Process Identification and Mapping
ABC Motors started by identifying key processes in its value chain, such as design and development, production, and supply chain management. Each process was carefully mapped out, defining inputs, outputs, responsibilities, and dependencies.
Step 2: Performance Metrics and Analysis
The organization established performance metrics for each process, focusing on aspects like defect rates, production cycle time, and customer satisfaction. ABC Motors utilized data analytics to track process performance and identify areas for improvement.
Step 3: Employee Empowerment
Employees were encouraged to actively participate in process improvement initiatives. Cross-functional teams were formed, consisting of representatives from different departments, who collaborated to identify process bottlenecks and implement solutions.
Step 4: Continuous Improvement and Innovation
ABC Motors embraced a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees to think innovatively and propose novel approaches to streamline processes. Ideas were evaluated, tested, and implemented, leading to significant efficiency gains.
Step 5: Supplier Collaboration
The company strengthened its relationships with suppliers, working together to ensure the consistent quality of raw materials and components. This collaboration resulted in a more reliable supply chain and reduced the risk of production disruptions.
Step 6: Technology Integration
ABC Motors invested in advanced manufacturing technologies, such as robotics and automation, to optimize its production processes. Additionally, data analytics tools provided real-time insights, allowing for agile decision-making.
Step 7: Performance Feedback and Customer Satisfaction
Feedback mechanisms were established to gather inputs from customers, dealers, and employees. The organization used this feedback to refine its processes and enhance product quality, resulting in higher customer satisfaction levels.
Step 8: Compliance and Certification
By implementing the process approach and adhering to IATF 16949:2016 requirements, ABC Motors achieved certification, demonstrating its commitment to quality excellence. This certification also enhanced the company's reputation and credibility among customers and partners.
Conclusion
The process approach is a powerful methodology for organizations seeking quality excellence in their operations. IATF 16949:2016 provides a robust framework to guide organizations towards process optimization, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement. By embracing the process approach, organizations can streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the automotive industry.



Comments